A gross lease, also called a full-service lease, means that the tenant is obliged to pay an agreed rent amount, and the landlord is responsible for self-paying all expenses for the property, including taxes, insurance, and maintenance.
However, another type of lease, a net lease frequently employed in Commercial Real Estate—shifts expenses from the landlord to the tenant. The tenant bears property taxes, insurance, and general maintenance costs.
Understanding the complexity of gross and net leases is vital for achieving a benefit and preventing exception obligations related to leases. In this blog, we will have a detailed look at the meaning of gross lease and net lease and the difference between the two.
What Is A Gross Lease?

A gross lease is an arrangement in which the tenant pays only the agreeable fixed rent to the landlord, and the landlord takes responsibility for all property-related costs. These are all occupational expenses, such as property taxes, insurance, and maintenance.
Tenants prefer a modified gross lease for its simplicity and transparency. Their monthly rental amount covers all their overhead costs, such as taxes and insurance. This allows property owners to handle the financial end of things. As such, it is an excellent choice for folks who would prefer a straightforward lease process where they are not worried about ever-changing expenditures.
What Is A Net Lease?

A net lease is a commercial real estate arrangement in which the lessor, the tenant, takes a specific property burden on top of the agreed-upon rent after a lease is granted. This provision involves various expenses, such as property taxes, insurance, and maintenance.
Depending on the type, lease nets could be single, double, or triple net, often redistributing financial responsibilities between Landlord and Tenant to a differing extent. A net lease is both lucrative and transparent, with the final rent of such leases communicated. Still, it is worthwhile to be cautious if one needs to check the terms correctly. This lease concept is found a lot in commercial places, thus making it appear as an alternative strategy to implement costs flexibly.
The Difference Between Gross Lease And Net Lease
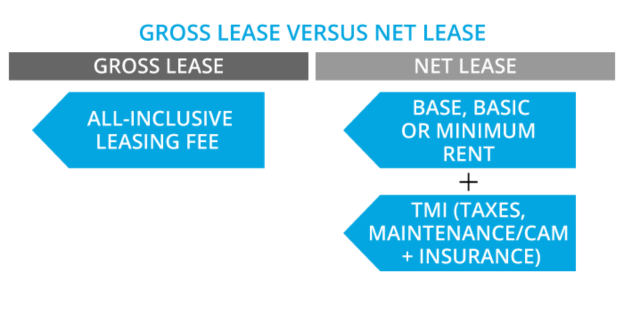
For the cases of commercial real estate leases, navigating between the gross lease and net lease is highly critical not only for landlords but also for tenants. These lease structures attribute the obligation of financial responsibility to different parties and predetermine the contract’s structure concerning the contract’s complexity and cost. We shall look into the principal disparities between a gross lease and a net lease here with the view of helping landlords and renters to get correct information.
1. Distribution of Costs
A significant difference between a gross lease and any other type is that the landlord bears all property-related costs. Total costs include taxes, insurance premiums, maintenance expenses, and utilities, among other operations expenditures. On the other hand, a net lease allocates operating costs between the landlord and the tenant, and the terms of the signed agreement set this allocation. In a single-tenant arrangement, the tenant’s responsibility covers property taxes, but in a double-net lease, the tenant will also cover its insurance costs. One of the primary forms of commercial real estate leasing is the triple net lease, which refers to the tenant’s obligation to pay property taxes, insurance charges, and maintenance bills.
2. Flexibility and Customization
A gross lease is an excellent idea for tenants as it will help keep them financially predictable. In these agreements, the tenants are supposed to read the contract and understand the terms and conditions only. There is no negotiating about sharing expenses related to the property because the landlord takes charge and bears all the charges. On the other hand, a net lease is one in which the tenant gets greater freedom to supervise- and manage property-related costs. Therefore, this level of particularization empowers the lessees to be in authority over maintenance, insurance firms, and taxes. On the one hand, the flexibility gives tenants more control, but on the other, the hands-on work is doubled because the tenant has to keep an eye on these additional costs and is required to administer the budget personally.
3. Risk and Responsibility
Leases structured as gross have the landlord subjecting the financial risk to see to the operating expenses. This configuration offers relaxation to the tenant on the part of electricity bills, maintenance, operational and repair costs, etc. Renters and floor owners, however, have equally a role in respecting each other’s interests and adjusting their expectations in the case of market changes. However, a Tenant in net lease arrangements possesses financial risks depending on the complex types of net leases. Concerning tenants, they feel the impact of rising property taxes and insurance premiums, along with an escalation in maintenance expenses.
4. Common Use Cases
The gross lease arrangement is widely applied to office leases, certain retail places, and some industrial buildings. when the landlord seeks to offer a comprehensive service to tenants by ensuring the site is ready to use. The most exciting thing about this contract structure is that it is ideal for tenants who prefer something other than lease structures that resemble complexities and unpredictable costs. Contrarily, commercial real estate often provides net leases, particularly for long-term agreements with significant retail tenants such as large fast-food chains, pharmacy stores, and square-shaped trading locations. Net lease, in particular, is highly suitable for the tenant to have more control over property-related expenses and a steady income for the investors.
Explore Various Gross Lease and Net Lease Property In The United States

Gross and net leases are the most preferable types of lease that a tenant looks for. Both offer small and large enterprises easy, affordable, and comfortable renting opportunities. But in this fast-growing world, finding a property for lease is very difficult according to one’s needs and preferences.
But now, technology has made finding a property for Lease in the US simple. You can visit Citadel Property Management Crop, a US-based real estate management firm offering tenants renting, leasing, and housing opportunities. Here, you can search for properties on gross or net leases per your preferences.
FAQs
1. Which is more beneficial, gross lease or net lease?
For a tenant, a gross lease is more beneficial. On the contrary, a net lease is more advantageous for a landlord.
2. What is the advantage of gross lease?
The disadvantage of the gross lease is that the overall rent cost includes the monthly maintenance charges.
4. What is the advantage of net lease?
The net lease offers an advantage by contributing to the property’s value increase and enabling the landlord to maximize rent.



